Важнейшей новостью вчера стали не nonfarm payrolls, а статья в Шпигеле, раскрывшая миру секрет о том, что Греция собралась выйти ез еврозоны, намеревается ввести собственную валюту и что переговоры о реструктуризации долгов Греции вот-вот начнутся.
Кризис в Греции принял драматический оборот.
Основные тезисы:
Проблемы Греции столь огромны, а антиправительственные выступления проходят почти каждый день, что премьер-министр Папандрео по-видимому решил что другого выхода не остается.
SPIEGEL ONLINE из германских правительственных источников получил информацию о том, что Греция рассматривает вопрос о выходе из еврозоны и введении своей собственной валюты.
Несколько ключевых министров финансов еврозоны и представителей ЕС соберутся в пятницу ночью в Люксембурге на секретную встречу.
Помимо желания выйти из еврозоны, министры будут обсуждать возможную реструктуризацию греческих долгов.
Германский министр финасов намерен отговорить Грецию от этого шага. В статьи перечисляются последствия, к которым это приведет.
К сожалению у нас редко оперативно осуществляют переводы столь важных документов, поэтому приходится его давать на английском языке: все-таки английский у нас знает гораздо больше читателей, чем немецкий.
Вот эта статья и ее перевод на английский язык.
And the original version of the article in native English:
The debt crisis in Greece has taken on a dramatic new twist. Sources with information about the government's actions have informed SPIEGEL ONLINE that Athens is considering withdrawing from the euro zone. The common currency area's finance ministers and representatives of the European Commission are holding a secret crisis meeting in Luxembourg on Friday night.
Greece's economic problems are massive, with protests against the government being held almost daily. Now Prime Minister George Papandreou apparently feels he has no other option: SPIEGEL ONLINE has obtained information from German government sources knowledgeable of the situation in Athens indicating that Papandreou's government is considering abandoning the euro and reintroducing its own currency.
Alarmed by Athens' intentions, the European Commission has called a crisis meeting in Luxembourg on Friday night. In addition to Greece's possible exit from the currency union, a speedy restructuring of the country's debt also features on the agenda. One year after the Greek crisis broke out, the development represents a potentially existential turning point for the European monetary union -- regardless which variant is ultimately decided upon for dealing with Greece's massive troubles.
Given the tense situation, the meeting in Luxembourg has been declared highly confidential, with only the euro-zone finance ministers and senior staff members permitted to attend. Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble of Chancellor Angela Merkel's conservative Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and Jörg Asmussen, an influential state secretary in the Finance Ministry, are attending on Germany's behalf.
'Considerable Devaluation'
Sources told SPIEGEL ONLINE that Schäuble intends to seek to prevent Greece from leaving the euro zone if at all possible. He will take with him to the meeting in Luxembourg an internal paper prepared by the experts at his ministry warning of the possible dire consequences if Athens were to drop the euro.
"It would lead to a considerable devaluation of the domestic currency against the euro," the paper states. According to German Finance Ministry estimates, the currency could lose as much as 50 percent of its value, leading to a drastic increase in Greek national debt. Schäuble's staff have calculated that Greece's national deficit would rise to 200 percent of gross domestic product after such a devaluation. "A debt restructuring would be inevitable," his experts warn in the paper. In other words: Greece would go bankrupt.
It remains unclear whether it would even be legally possible for Greece to depart from the euro zone. Legal experts believe it would also be necessary for the country to split from the European Union entirely in order to abandon the common currency. At the same time, it is questionable whether other members of the currency union would actually refuse to accept a unilateral exit from the euro zone by the government in Athens.
What is certain, according to the assessment of the German Finance Ministry, is that the measure would have a disastrous impact on the European economy.
"The currency conversion would lead to capital flight," they write. And Greece might see itself as forced to implement controls on the transfer of capital to stop the flight of funds out of the country. "This could not be reconciled with the fundamental freedoms instilled in the European internal market," the paper states. In addition, the country would also be cut off from capital markets for years to come.
In addition, the withdrawal of a country from the common currency union would "seriously damage faith in the functioning of the euro zone," the document continues. International investors would be forced to consider the possibility that further euro-zone members could withdraw in the future. "That would lead to contagion in the euro zone," the paper continues.
Banks at Risk
Moreover, should Athens turn its back on the common currency zone, it would have serious implications for the already wobbly banking sector, particularly in Greece itself. The change in currency "would consume the entire capital base of the banking system and the country's banks would be abruptly insolvent." Banks outside of Greece would suffer as well. "Credit institutions in Germany and elsewhere would be confronted with considerable losses on their outstanding debts," the paper reads.
The European Central Bank (ECB) would also feel the effects. The Frankfurt-based institution would be forced to "write down a significant portion of its claims as irrecoverable." In addition to its exposure to the banks, the ECB also owns large amounts of Greek state bonds, which it has purchased in recent months. Officials at the Finance Ministry estimate the total to be worth at least €40 billion ($58 billion) "Given its 27 percent share of ECB capital, Germany would bear the majority of the losses," the paper reads.
In short, a Greek withdrawal from the euro zone and an ensuing national default would be expensive for euro-zone countries and their taxpayers. Together with the International Monetary Fund, the EU member states have already pledged €110 billion in aid to Athens -- half of which has already been paid out.
"Should the country become insolvent," the paper reads, "euro-zone countries would have to renounce a portion of their claims."
Все, что здесь написано, звучит очень сильно и тревожно.
Последовали многочисленные официальные опровержения, но факт остается фактом: нет дыма без огня. Шпигель не стал бы распускать столь беспочвенных слухов.
Рынки уже отреагировали на эту новость. Евро снизился на две фигуры относительно доллара, S&P500 тоже развернулся и до закрытия успел пройти 20 пунктов вниз.
Интересно, что все почти в точности повторяется, как в прошлом году. Тогда тоже в мае разразился греческий кризис и ей потребовалось оказание помощи.
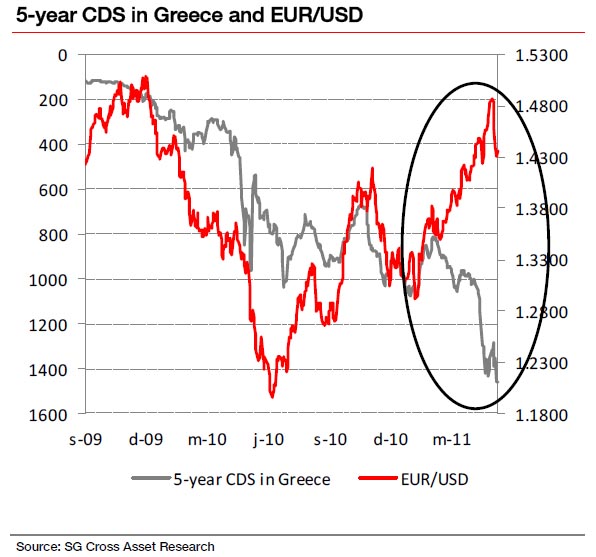
Обращает на себя внимание очень сильная дивергенция, которая возникла в последнее время между евро и оценкой рисков неплатежеспособности ( CDS Греции, да и других PIIGS). Если раньше они относительно хорошо коррелировали между собой, то теперь графики просто разошлись совершенно в разные стороны. На мой взгляд, это говорит о том, что выход Греции уже не рассматривается как риск для дальнейшего существования еврозоны. Загнанных лошадей пристреливают, не правда ли...
Несомненно выход из еврозоны будет иметь драматические последствия для самой Греции и поэтому маловероятно, что она это сделает это по собственной воле.
Для этого есть следующие доводы:
В настоящий момент Греция хорошо обеспечена ликвидностью до 2013 года, имеется еще 83 млрд. евро в фондах ЕС и МВФ, зарезервированных под Грецию.
Помимо всего прочего ¼ долга (это на самом деле немало) сосредоточено внутри страны: социальная защита (28 млрд. евро), банки ( 31 млрд.) и даже домашние хозяйства держат 6 млрд. евро греческого долга.
Поэтому скорее всего речь на переговорах пойдет о реструктуризации.
Будем следить за тем, что будет дальше. Читайте комментарии...
